LeetCode222 完全二叉树节点数
This page is not available in English yet. (つд⊂)
题目
According to Wikipedia, every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled in a complete binary tree, and all nodes in the last level are as far left as possible. It can have between
1and2hnodes inclusive at the last levelh.Design an algorithm that runs in less than
O(n)time complexity.
这个需求的暴力解法是遍历一遍,时间复杂度 尚可接受,但这样就失去了这题的意义。这里实现一个时间复杂度为 的算法。
计算上部节点数
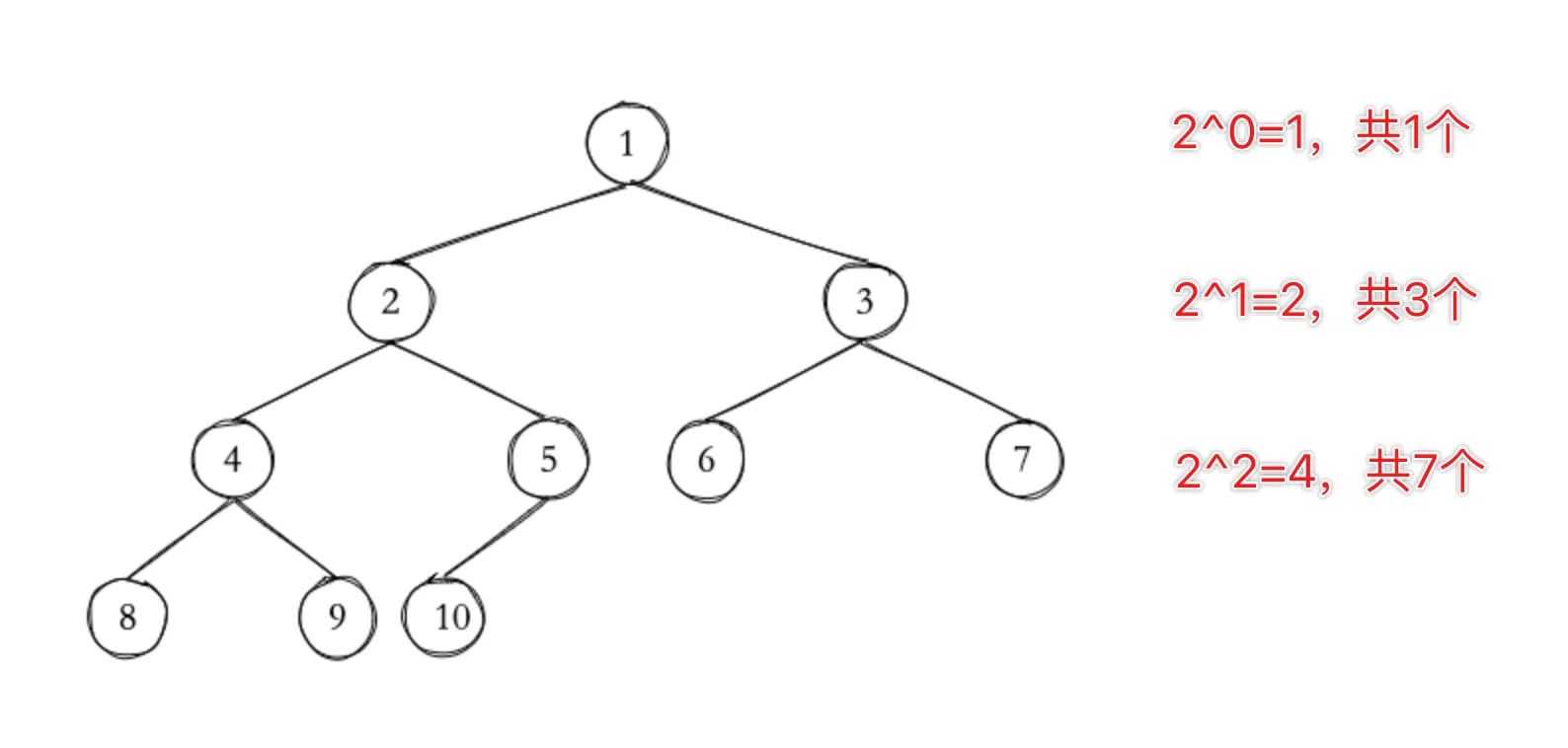
不难得出以下结论:
- 第 h 层的节点数为 (h 从 1 开始)
- 从根节点到第 h 层总节点数为 (h 从 1 开始)
那么只要知道了树的高度,就可以立即求出除了最后一层外的节点总数。同时鉴于完全二叉树的特性,只需一直向左子树遍历就可以得到高度。
// 求完全二叉树的高度
private int height(TreeNode root) {
int res = 0;
while (root != null) {
res++;
root = root.left;
}
return res;
}计算底层节点数
寻找最后一个节点
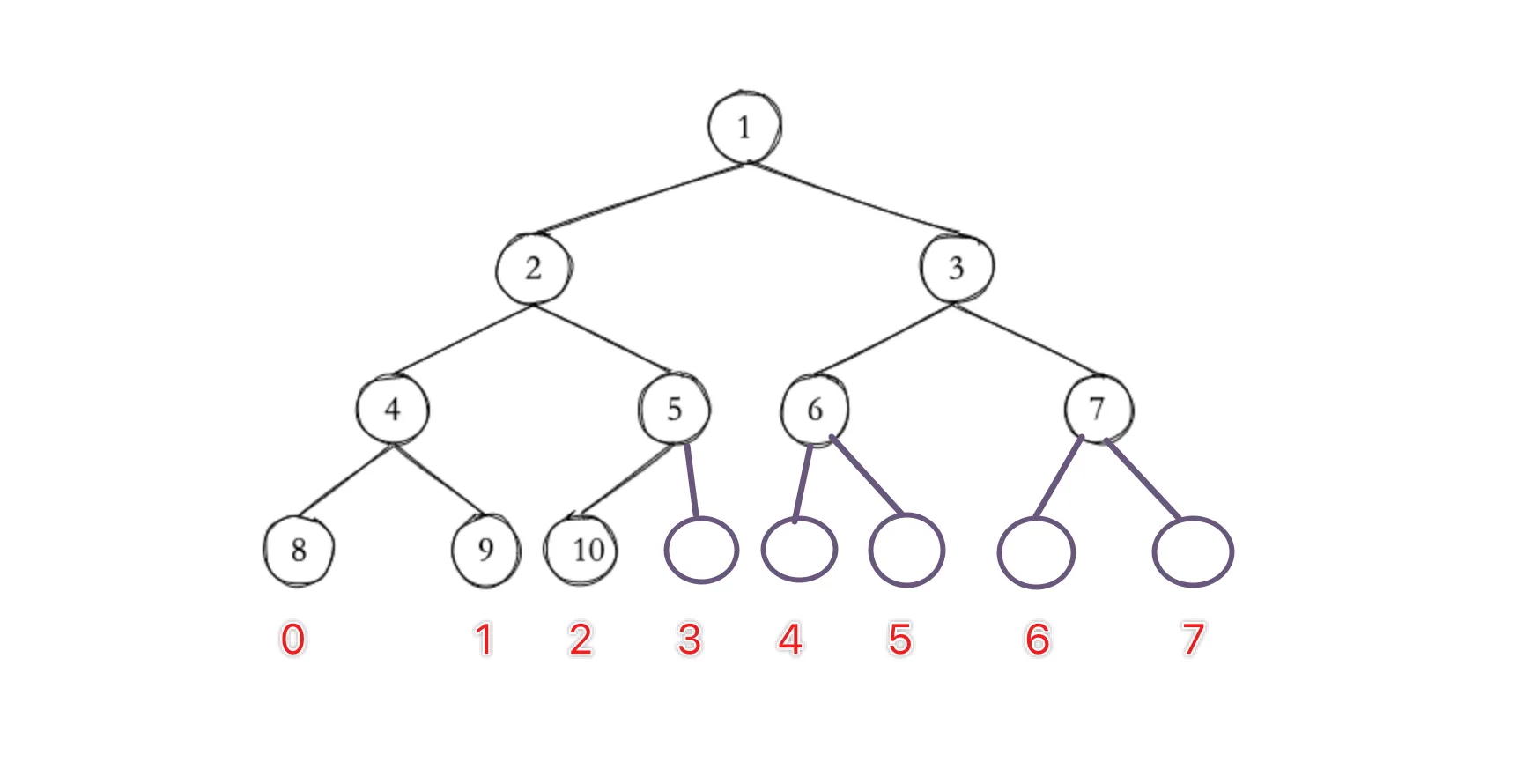
如图所示,我们给底层节点编号(包括不存在的节点),形式上把它们视为有序数组。也就是说,只需在 时间复杂度内从这个数组中找到最后一个存在的节点就行。这个需求很轻松地联想到二分查找。
不过需要对二分查找做一点修改:
private int findLastNodeIndex(TreeNode root, int height) {
// 搜索区间 [l,r]
int l = 0, r = (int) (Math.pow(2, height - 1) - 1);
int result = 0;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (nodeExists(root, height, mid)) {
result = mid;
l = mid + 1;
} else {
r = mid - 1;
}
}
return result;
}为什么需要额外一个变量 result? 在本题的场景下,二分查找最终一定会收缩到两个相邻的节点,此时 mid 指向靠左的那个,如果它存在则需要进一步确认它右边的那个是否存在。如果右边的不存在就需要回退到左边,因此需要一个变量存储左边的下标。
通过下标寻找节点
二分查找要求可以通过下标来找到元素,显然二叉树不满足这个要求,还得编写额外的函数来实现。
我们可以把整个二叉树看作是一个标准二分查找的执行过程。现在知道了目标节点的下标,只需把它和当前搜索区间的中点进行对比,再决定往左还是往右查找就行了。
/**
* 判断最后一行下标为 index 的节点是否存在。index 从 0 开始。
* @param height 树的高度
*/
private boolean nodeExists(TreeNode root, int height, int index) {
int l = 0, r = (int) (Math.pow(2, height - 1) - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < height - 1; i++) {
// 循环过程中 root 不可能为空
// 因为完全二叉树除了最后一行,每一行都是满的
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
// 这里必须是小于等于
// mid 与 index 相等时必有 r=l+1, index=l,显然应该向左
if (index <= mid) {
root = root.left;
r = mid - 1;
} else {
root = root.right;
l = mid + 1;
}
}
return root != null;
}代码(java)
时间复杂度分析:
- 求树高的时间复杂度为
- 最后一层最多有 个节点,它几乎是总节点数的一半。同时考虑二分算法,可得出寻找最后一个节点的时间复杂度为
- 寻找最后一个节点时,每一次利用下标取节点的时间复杂度均为
因此总体时间复杂度为
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int height = height(root);
// 忽略最后一层的节点数
int count1 = (int) Math.pow(2, height - 1) - 1;
return count1 + findLastNodeIndex(root, height) + 1;
}
private int height(TreeNode root) {
int res = 0;
while (root != null) {
root = root.left;
res++;
}
return res;
}
private int findLastNodeIndex(TreeNode root, int height) {
// 搜索区间 [l,r]
int l = 0, r = (int) (Math.pow(2, height - 1) - 1);
int result = 0;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (nodeExists(root, height, mid)) {
result = mid;
l = mid + 1;
} else {
r = mid - 1;
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 判断最后一行下标为 index 的节点是否存在。index 从 0 开始。
* @param height 树的高度
*/
private boolean nodeExists(TreeNode root, int height, int index) {
int l = 0, r = (int) (Math.pow(2, height - 1) - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < height - 1; i++) {
// 循环过程中 root 不可能为空
// 因为完全二叉树除了最后一行,每一行都是满的
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
// 这里必须是小于等于
// mid 与 index 相等时必有 r=l+1, index=l,显然应该向左
if (index <= mid) {
root = root.left;
r = mid - 1;
} else {
root = root.right;
l = mid + 1;
}
}
return root != null;
}
}